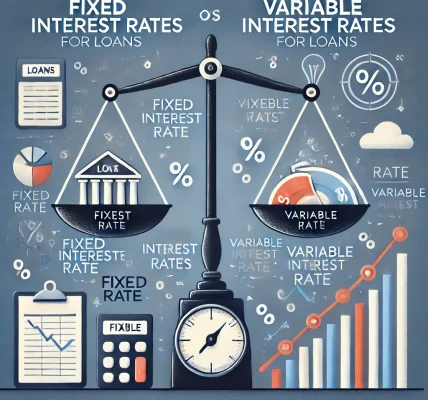
When applying for a loan, one of the most crucial decisions is choosing between fixed and variable (floating) interest rates. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and selecting the right one depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
1. What is a Fixed Interest Rate?
A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan tenure. Regardless of market fluctuations, your EMI (Equated Monthly Installment) stays the same, providing stability and predictability.
✅ Pros of Fixed Interest Rates:
✔️ Stable EMIs: Your monthly payments won’t change, making budgeting easier.
✔️ No Market Risk: You are protected from interest rate hikes.
✔️ Better for Long-Term Planning: Ideal for salaried individuals with a fixed income.
❌ Cons of Fixed Interest Rates:
❌ Higher Initial Rates: Fixed rates are usually higher than variable rates.
❌ No Benefit from Rate Drops: If market rates fall, you won’t get a lower rate.
❌ Prepayment Charges: Many banks charge penalties for early loan closure.
2. What is a Variable (Floating) Interest Rate?
A variable interest rate fluctuates based on market conditions, typically linked to a benchmark rate like the repo rate or MCLR (Marginal Cost of Funds-Based Lending Rate).
✅ Pros of Variable Interest Rates:
✔️ Lower Initial Rates: Floating rates are generally cheaper than fixed rates.
✔️ Benefit from Rate Cuts: If interest rates fall, your EMI reduces.
✔️ Long-Term Savings: Over time, you may pay less than a fixed-rate loan.
❌ Cons of Variable Interest Rates:
❌ Unpredictable EMIs: Your monthly payments may increase if rates rise.
❌ Higher Financial Risk: If the market sees an interest rate surge, your loan becomes expensive.
❌ Not Ideal for Short-Term Loans: If rates increase within a short period, you might pay more.
3. Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Fixed Interest Rate | Variable Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Stability | Remains constant | Fluctuates with market |
| Initial Interest Rate | Higher | Lower |
| EMI Amount | Fixed | Can increase or decrease |
| Best For | Stability, long-term planning | Market fluctuations, potential savings |
| Risk Factor | Low | High |
| Effect of Rate Cuts | No benefit | EMI reduces |
| Effect of Rate Hikes | No impact | EMI increases |
4. Which One Should You Choose?
✔ Choose Fixed Interest Rate If:
- You prefer stability in EMIs.
- You are taking a long-term loan (home loan, business loan).
- You don’t want to take market risks.
✔ Choose Variable Interest Rate If:
- You can handle EMI fluctuations.
- You expect interest rates to drop in the future.
- You are taking a short-term loan and want lower initial payments.
Final Verdict
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. If you prioritize stability, go for fixed interest rates. If you want potential savings and can manage risks, variable interest rates might be better.
📌 Pro Tip: Some lenders offer a hybrid loan, which starts with a fixed rate for a few years and then shifts to a variable rate. This can be a great middle-ground option!