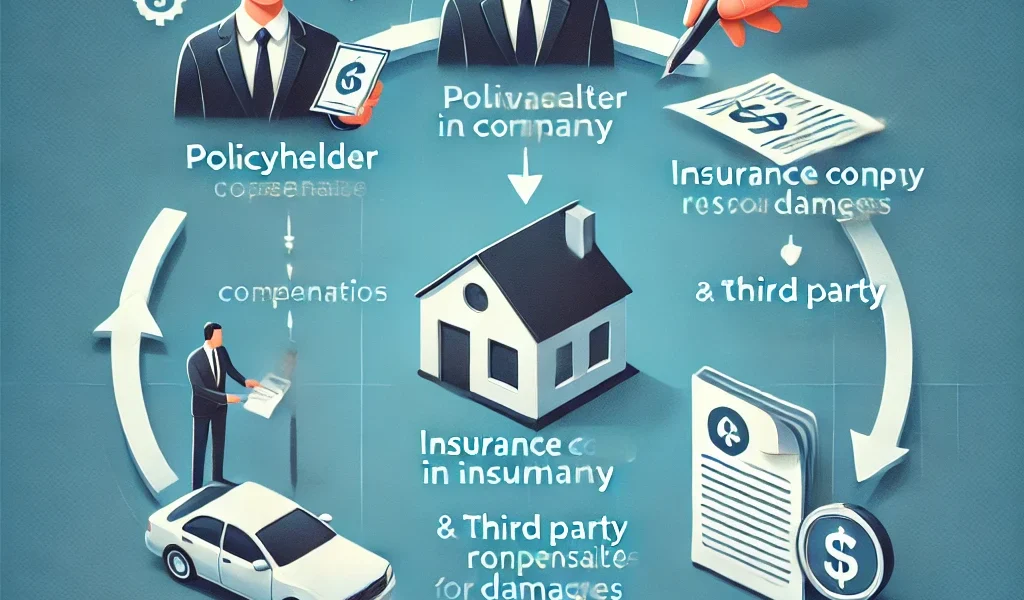
Insurance claims can be complex, and one of the most misunderstood aspects of the process is subrogation. Whether you’re dealing with a car accident, property damage, or health insurance claim, subrogation plays a crucial role in determining how claims are settled and whether you might receive additional compensation.
In this DIY guide, we’ll break down what subrogation means, how it impacts your insurance claim, and what steps you should take to protect your rights and maximize your claim payout.
1. What is Subrogation?
Subrogation is a legal process where an insurance company steps into the shoes of its policyholder to recover costs from a third party responsible for the damages. Essentially, your insurance company pays your claim upfront and then seeks reimbursement from the party at fault.
Example of Subrogation:
- You get into a car accident that was caused by another driver.
- Your insurance company pays for your repairs and medical expenses.
- Your insurance provider then sues or negotiates with the at-fault driver’s insurance company to recover the money they paid on your behalf.
- If they recover more than what they paid, you may be entitled to additional compensation.
2. How Does Subrogation Work?
Step 1: Insurance Pays Your Claim
Once you file a claim, your insurer processes it and issues payment based on your policy coverage.
Step 2: Investigation of Fault
The insurance company investigates to determine if another party is liable for the damages.
Step 3: Recovery Efforts
If a third party is responsible, your insurer will initiate subrogation to recover their costs. This may involve negotiations or legal action against the at-fault party’s insurer.
Step 4: Settlement and Potential Refund
If the insurer successfully recovers more than they paid, you may receive a deductible reimbursement or additional compensation.
3. Why is Subrogation Important?
Subrogation benefits both insurance companies and policyholders by:
- Keeping insurance premiums lower by recovering costs from at-fault parties.
- Ensuring that responsible parties bear financial responsibility for damages.
- Helping you recover your deductible if the at-fault party is successfully pursued.
4. Common Types of Insurance Claims Involving Subrogation
1. Auto Insurance Claims
- If another driver is at fault, your insurer will seek reimbursement from their insurer.
- You may receive a refund of your deductible if the claim is successful.
2. Property Insurance Claims
- If your home is damaged due to a contractor’s negligence, your insurance company may recover costs from them.
- Example: A faulty plumbing job causes a leak—your insurer covers repairs and then sues the plumber’s liability insurance.
3. Health Insurance Claims
- If you’re injured in an accident and your health insurer covers medical bills, they may seek reimbursement from the at-fault party’s auto or liability insurance.
4. Workers’ Compensation Claims
- If you’re injured at work due to a third party’s negligence (e.g., faulty equipment), your workers’ compensation insurer may pursue subrogation against the manufacturer.
5. What Are Your Rights in Subrogation?
Understanding your rights can help you maximize your compensation and avoid legal pitfalls.
1. Right to Be Notified
- Your insurer must inform you if they intend to pursue subrogation.
- Always review any correspondence from your insurer regarding recovery efforts.
2. Right to Deductible Reimbursement
- If your insurer successfully recovers money from the at-fault party, you should receive a refund of your deductible.
- Keep records of your payments and claim details.
3. Right to Negotiate
- If you receive a settlement offer, you may be able to negotiate better terms before agreeing to subrogation recovery.
- Consult with an attorney if you’re unsure about the terms.
4. Right to Opt-Out in Some Cases
- Some policies allow policyholders to opt out of subrogation if they wish to pursue their own legal action.
- Check your policy for waiver of subrogation clauses.
6. How to Protect Yourself During Subrogation
1. Understand Your Policy
- Read your insurance policy’s subrogation clause to know your rights and obligations.
2. Keep All Records
- Maintain accident reports, medical bills, receipts, and insurance correspondence.
3. Cooperate with Your Insurer
- Providing accurate and timely information can speed up the subrogation process.
4. Seek Legal Advice If Needed
- If you receive a large settlement or are unsure about legal terms, consult with an insurance lawyer.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I prevent my insurance company from pursuing subrogation?
- In most cases, no. However, you may be able to negotiate certain terms or opt out if specified in your policy.
Q2: What happens if the at-fault party refuses to pay?
- Your insurance company may take legal action to recover funds, or in some cases, write off the loss.
Q3: How long does subrogation take?
- The process can take anywhere from a few months to a couple of years, depending on the complexity of the case and legal proceedings.
Q4: What should I do if I get a subrogation notice?
- Review the notice carefully and confirm the details with your insurer. If you disagree, seek legal advice before signing anything.
8. Conclusion
Subrogation is an essential part of the insurance claims process that helps both policyholders and insurers recover costs fairly. Understanding how subrogation works can help you protect your rights, recover your deductible, and maximize your claim payout.
Always review your policy, keep accurate records, and seek legal advice if necessary to ensure that you receive the full benefits of your insurance coverage.
By staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the complexities of subrogation with confidence and ensure that your claim is handled fairly and efficiently.